Orsiro™ Mission™
Delivering superiority.1,a

Thank you for your interest in Orsiro™ Mission™ DES. Please provide your contact details and a representative will reach out shortly.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
- ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
- High Bleeding Risk (HBR)
- One Month of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) in HBR Patients
- Calcified Lesions (moderate/severe calcification)
- Complex Lesions (B2/C)
- Long Lesions (LL) (e.g. ≥ 20 mm)
- Small Vessels (SV) (e.g. ≤ 2.75 mm)
- Multi-Vessel Disease (MVD) Male/Female Old Patients (e.g. > 65 y)

The next level of deliverability²
1st in Push3, 1st in Track3, 1st in Cross3
Ultrathin struts⁴
Outstanding patient outcomes6,b
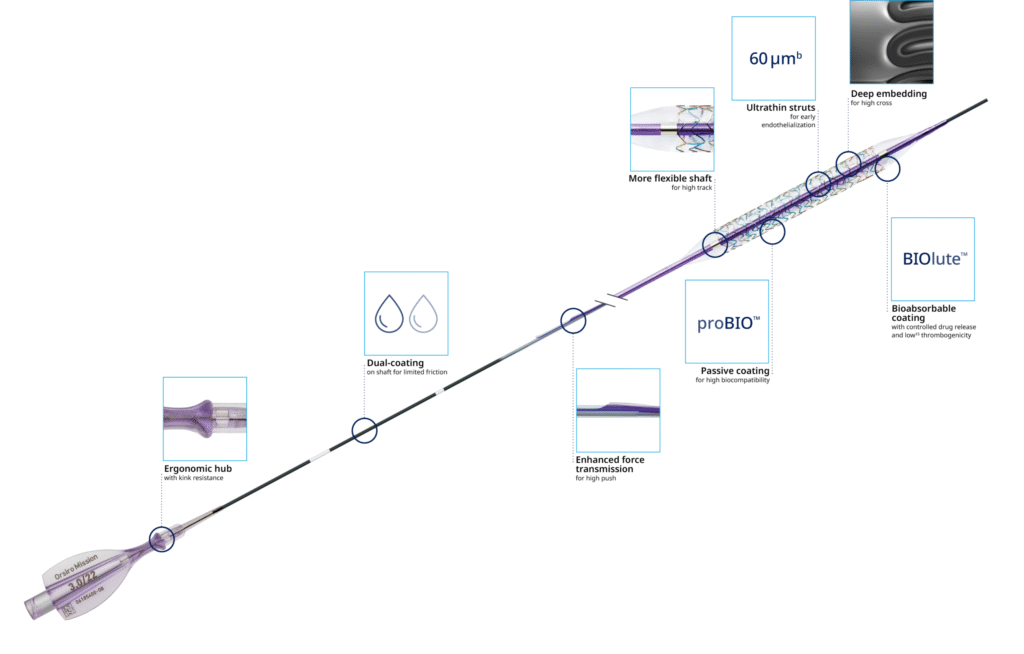
Product Highlights
The next level of deliverability²

1st in Push³
Transmitting up to 96% more force from hub to tip.

1st in Track3
Up to 33% less force needed to follow the path to the lesion.
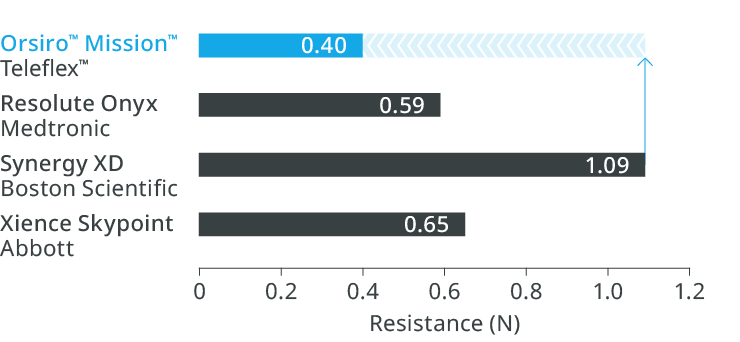
1st in Cross3
Up to 64% less force needed to successfully cross demanding anatomies.
Ultrathin struts4
For early endothelialization5
Conforming to a wider range of vessels7,f
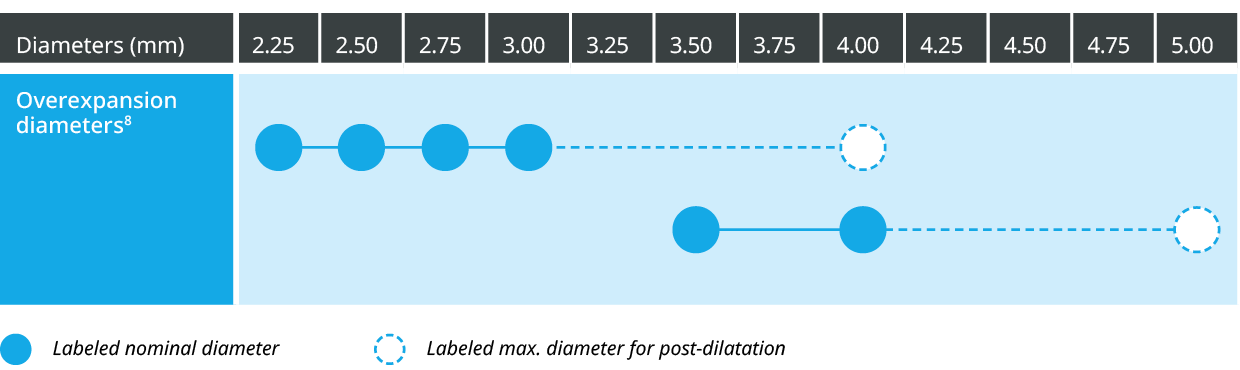
Strut thickness in perspective8

Early endothelialization5

Outstanding patient outcomes6,b

Orsiro™
family of DES – One of the most studied DES14,b,i

Continued superiority in STEMI at 5 years15,b
Product Overview
Clinical Studies Overview
BIOSTEMI
Proven superiority with Orsiro™ DES in STEMI patients up to 5 yearsi,l
- Study Type – RCT
- Patients – 1300
- Status – Completed, 60-months FU available
- Primary Endpoint – TLF at 12 months
BIO-FLOW DAPT
Proven safety and efficacy for Orsiro™ Mission™
DES with 1-month DAPT17,i,k
- Study Type – RCT
- Patients – 1948
- Status – 12-month FU available
- Primary Endpoint – Composite of Cardiac death, Myocardial Infarction and Definite or probable Stent thrombosis at 12 months
BIOFLOW-V
Orsiro™ ultrathin struts DES, pushing the boundaries of safety performance18
- Study Type – RCT
- Patients – 1334
- Status – Completed, 60-months FU available
- Primary Endpoint – TLF at 12 months
Outstanding Patient Outcomes6,b

STEMI = ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
a. Data on file (n = 5), based on statistically significant differences on the bench for Pushability, Trackability, and Crossability compared to Xience Skypoint, superior to Xience in STEMI patients; b. Clinical data collected with Orsiro DES device within the Orsiro DES family clinical program; c. In comparison to Xience, based on TLF with Orsiro DES; d. In comparison to Resolute Onyx, Data on file; e. In comparison to Synergy XD, data on file; f. Always refer to the Instructions for Use (IFU) for the Maximum Diameter for post-dilation applying in your country; g. Ø 2.25-3.0 mm strut thickness 60 µm, Ø 3.5-4.0 mm strut thickness 80 µm; h. Images: Secco G et al. Time-related changes in neointimal tissue coverage following a new generation SES implantation: an OCT observational study. Presented at: euro PCR, May 20, 2014; Paris, France, i. Clinical data collected with Orsiro Mission DES device within the Orsiro DES family clinical program, j. At 5-year in STEMI patients, k. Please refer to the IFU for indications and post-procedure antiplatelet therapy recommendations; l. Target Lesion Failure at 5-year follow-up Orsiro DES: 7.7%, Xience DES: 11.1%, BIOSTEMI with historical information RR, 0.70; 95% BCI, 0.51-0.95, Bayesian posterior probability, 0.988, difference: -31%.
1. Iglesias JF. et al, Long-term outcomes with biodegradable polymer sirolimus eluting stents versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: 5-year follow-up of the BIOSTEMI randomized superiority trial, The Lancet, 2024; 2. In comparison to Xience Sierra, Resolute Onyx and Synergy for bench tests on pushability, trackability and crossability, data on file; 3. In comparison to Resolute Onyx, Xience Sierra and Synergy, data on file; 4. As characterized with respect to strut thickness in Bangalore et al. Meta-analysis; 5. Per investigators’ interpretation in Secco et al. Imaging data serial observations. Secco GG et al. Time-related changes in neointimal tissue coverage of a novel Sirolimus eluting stent: Serial observations with optical coherence tomography. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine. 2016; 17(1): 38-43; 6. Based on investigator’s interpretation of BIOFLOW-V endpoint results; 7. Based on Kapoor A. et al., The road to the ideal stent: A review of stent design optimization methods, findings, and opportunities, Materials&Design, 2024; 8. Stefanini GG et al. Coronary stents: novel developments. Heart. 2014 Jul 1;100(13):1051-61; 9. Low AF. Stent platform for procedural success: Introducing the Continuous Sinusoidal & Core Wire Technologies. Presented at: AsiaPCR; 22-24 January, 2015; Singapore, Singapore; 10. Tolentino A. Evolving DES Strategy: Biodegradable Polymer vs. Bioabsorbable Scaffold. Presented at: Cardiovascular Nurse/Technologist Symposium; June 17, 2016; New York, USA; 11. Secco G et al. Time-related changes in neointimal tissue coverage of a novel Sirolimus eluting stent: Serial observations with optical coherence tomography. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine 17.1 (2016): 38-43; 12. Iglesias J et al. Biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (BIOSTEMI): a single-blind, prospective, randomised superiority trial. The Lancet. 2019 Sep 2.; 13. Data on file, status February 2023; 14. In large RCTs, based on Taglieri et al. Meta-analysis, against currently used DES; 15. Based on TLF primary endpoint. Iglesias, JF. et al. Long-term outcomes with biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: 5-year follow-up of the BIOSTEMI randomized superiority trial, presented at TCT 2023; 16. Kandzari D et al. Ultrathin Bioresorbable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stents versus Thin Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stents for Coronary Revascularization: Final 5-year Outcomes from the Randomized BIOFLOW V Trial, Submitted manuscript to JACC, 2022: NCT02389946; 17. Valgimigli M et al. Circulation 2023 Aug 25; 18. Taglieri N et al. Target lesion failure with current drug-eluting stents evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis. JACC 2020.
Teleflex, the Teleflex logo, BIOlute, Orsiro, Orsiro Mission and proBIO are trademarks or registered trademarks of Teleflex Incorporated or its affiliates, in the U.S. and/or other countries. All other names are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Information in this material is not a substitute for the product Instructions for Use. Not all products may be available in all countries. Please contact your local representative. Revised 09/2025. ©2025 Teleflex Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Specifications are subject to modification, revision and improvement.