Pulsar™-18 T3
Self-Expanding Stent System
Clinically proven.1-5 Effortless precision.6,7
Register for a downloadable PDF of case reports to see what can be achieved with the Pulsar™-18 T3 by providing your contact details below. This will also enable your local sales organization follow up with you via e-mail.
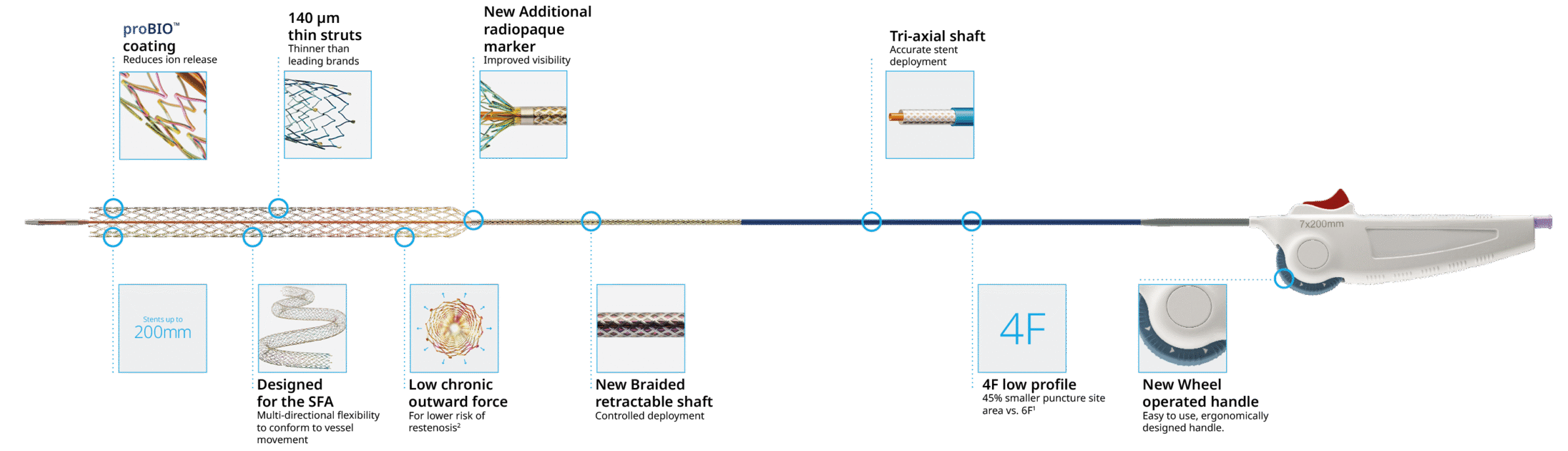
Key Benefits
Accurate stent deployment6,7
Tri-axial system with braided shaft
Lower risk of restenosis8
Thin struts, low COFSmaller puncture site area
Low profile delivery system
Clinically proven even in complex lesions9
Positive results even for long and occluded lesions in a high risk population

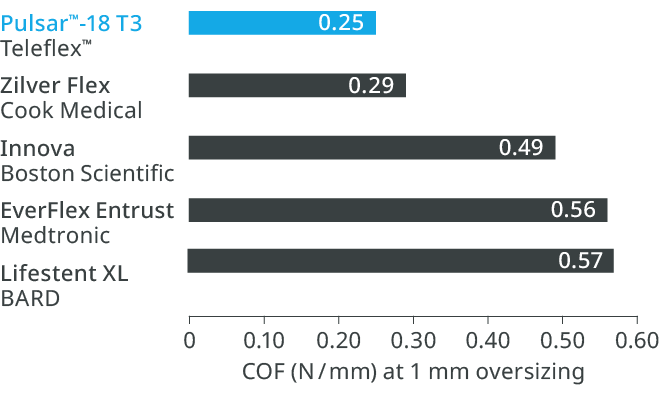
What is Chronic Outward Force (COF) and why does it matter?
Chronic Outward Force (COF) is the force exerted on the vessel wall by a self-expanding stent to achieve its present diameter.11 Thinner struts, which have lower COF, result in a lower risk of restenosis, reduced vessel injury and inflammation and faster endothelialization.8,12,13
Thinner struts for lower COF14
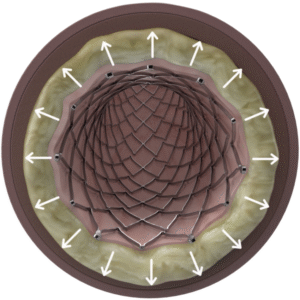
Benefits of low COF:
- Lower risk of restenosis8
- Reduced vessel injury and inflammation12
- Faster endothelialization13
Easy to use, intuitive wheel operated handle.
The first tri-axial, 4F thin-strut stent system for the treatment of lower limb peripheral arterial disease.
1. BIOFLEX-I SSED, data on file; 2. Bosiers M. et al. 4-French–compatible endovascular material is safe & effective in the treatment of femoropopliteal occlusive disease: Results of the 4EVER Trial. J ENDOVASC THER 2013; 20:746-756; 3. Lichtenberg M. et al. PEACE I All-Comers Registry: Patency Evaluation After Implantation of the 4-French Pulsar-18 Self-Expanding Nitinol Stent in Femoropopliteal Lesions. J ENDOVASC THER 2014; 21:373–380; 4. Lichtenberg M. Superficial Femoral Artery TASC D registry: 12-month effectiveness analysis of the Pulsar-18 SE nitinol stent in patients with critical limb ischemia. J Cardiovasc Surg. 2013; 54:433-9; 5. Lichtenberg et al. Evaluation of the 4-French Pulsar-18 Self-expanding Nitinol Stent in Long Femoropopliteal Lesions. Clinical Medicine Insights: Cardiology 2014:8(S2) 37–42 doi: 10.4137/CMC.S15224; 6. Evaluation of Market Acceptance 162091, data on file; 7. Accuracy of Stent Placement Design Verification and Validation 145265, data on file; 8. Zhao HQ Late stent expansion and neointimal proliferation of oversized nitinol stents in peripheral arteries. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009; 32(4); 720-6; 9. Bosiers M 4EVER 24m: long-term results of 4F Pulsar stent. Presented at: Cirse, 2013. Barcelona,Spain; 10. Lichtenberg et al. Effectiveness of the Pulsar-18 self-expanding stent with optional drug-coated balloon angioplasty in the treatment of femoropopliteal lesions – the BIOFLEX PEACE All-Comers Registry. Vasa (2019), 1-9. doi_10.10240301- 1526a000785; 11. Freeman JW, et al. A link between stent radial forces and vascular wall remodeling: the discovery of an optimal stent radial force for minimal vessel restenosis. Connect Tissue Res. 2010 Aug; 54(4): 314-26; 12. Koskinas C. Role of endothelial shear stress in stent restenosis and thrombosis: pathophysiologic mechanisms and implications for clinical translation. JACC 2012 10;59(15):1337-49; 13. Koppara T. Thrombogenicity and early vascular healing response in metallic biodegradable polymer-based and fully bioabsorbable drug-eluting stents. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2015 8(6):e002427; 14. data on file. 6.0 mm diameters. Supera stent not possible to test due to its design and applied test method.
Teleflex, the Teleflex logo, proBIO and Pulsar are trademarks or registered trademarks of Teleflex Incorporated or its affiliates in the U.S and/or other countries. All other names are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. Refer to this IFU link for a copy of the Instructions for Use and for a complete listing of the indications, contraindications, warnings and precautions. Information in this material is not a substitute for the product Instructions for Use. Not all products may be available in all countries.
© 2025 Teleflex Incorporated. All rights reserved. Revised 9/2025.
